The promise of Industry 4.0 conceptualizes rapid changes in technology and operating processes. Today, interconnectivity through cyber-physical systems and efficient data harnessing assumes central focus across industries. This holds especially true in the manufacturing industry, giving rise to smart manufacturing in smart factories.
Before we delve deeper into what organizations need to do to disrupt their processes and secure a firm footing at the forefront of innovation, a conceptual understanding of smart manufacturing is essential. Smart manufacturing is a technology-driven approach to manufacturing that adopts the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) - an extension of the Internet of Things (IoT) in industrial sectors and applications. With a strong focus on machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, big data, predictive maintenance, and machine learning, IIoT enables industries and enterprises to promote enhanced efficiency and reliability in their operations. The IIoT encompasses industrial applications such as industrial robotics, medical equipment operations, and software-defined production processes.
The advent of IIoT-driven smart manufacturing envisions a production environment with a fully automated and intelligent network of systems that facilitates machines, facilities, and logistics chains within the manufacturing plant to be managed with little to no manual intervention. In other words, the establishment of a smart factory. The active exchange of data between production tools, machines, and all elements within the production technology chain through embedded sensor systems, fuels machine learning to optimize operations by boosting efficiency and realizing more savings continually. Additionally, the associated benefits for organizations adopting smart manufacturing technologies are as follows:
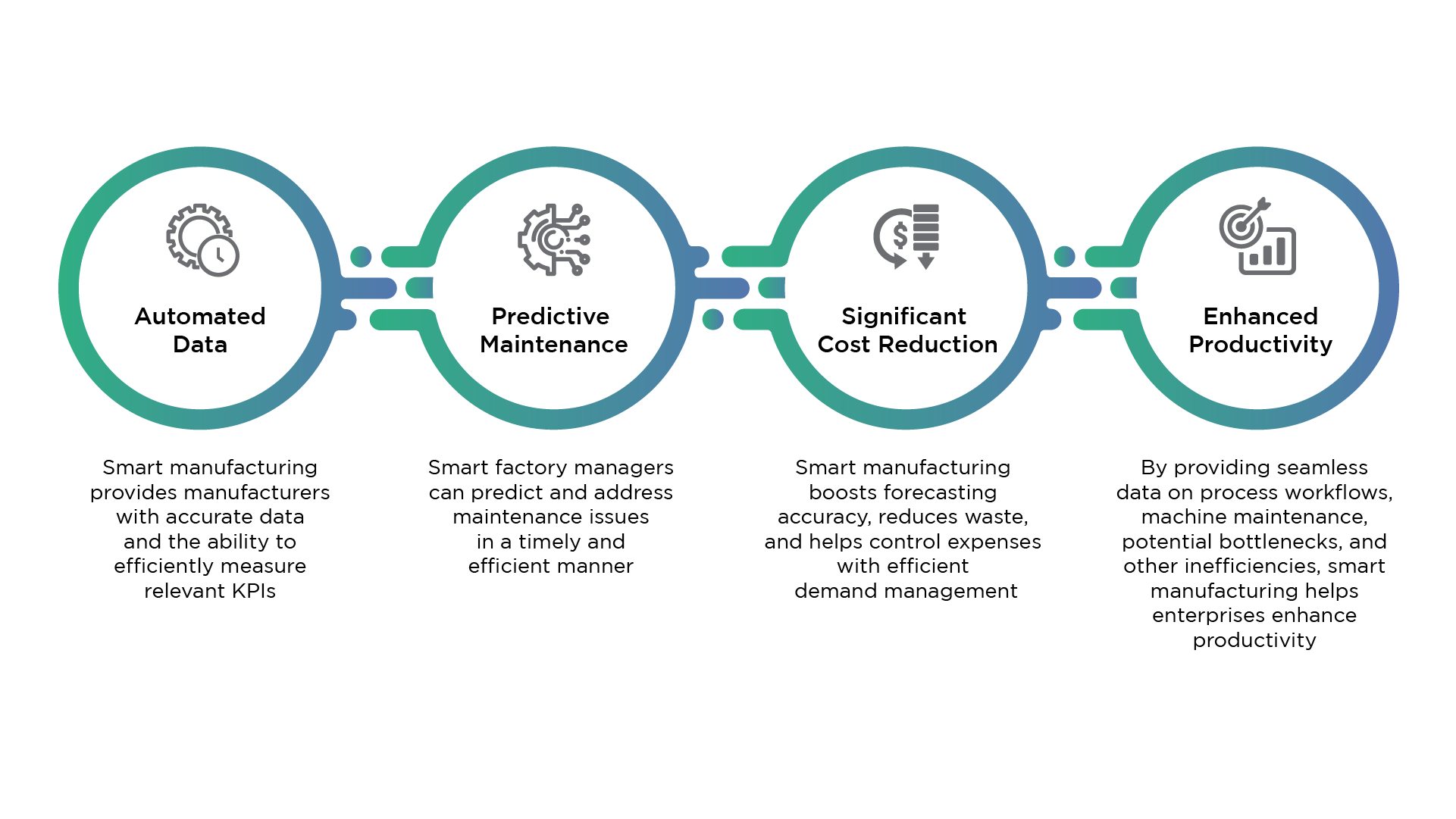
Key Market Trends For Smart Manufacturing
The growing awareness of smart manufacturing and its associated benefits have characterized a paradigm shift in the manufacturing market. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global smart manufacturing market is expected to grow from USD 277.81 billion in 2022 to USD 658.41 billion in 2029 at a CAGR of 13.1%. Global manufacturers recognize that the next generation of robotics and automation technologies within the ambit of smart manufacturing will have an unprecedented impact on manufacturing in terms of productivity, quality, safety, and cost metrics. According to Cisco, machine-to-machine (M2M) connections that support IoT applications account for more than half of the world’s 28.5 billion connected devices. Interestingly, the largest market share of smart factories is held by APAC countries with China and Japan leading the way.
A recent study by Forbes found that enterprises invested an annual average of 3.24% of their revenue by building 40% more smart factories over the last three years, almost 1.7 times higher than the amount invested between 2016-2019. As of 2021, smart manufacturing technologies have made a foray into most production-defined industries.
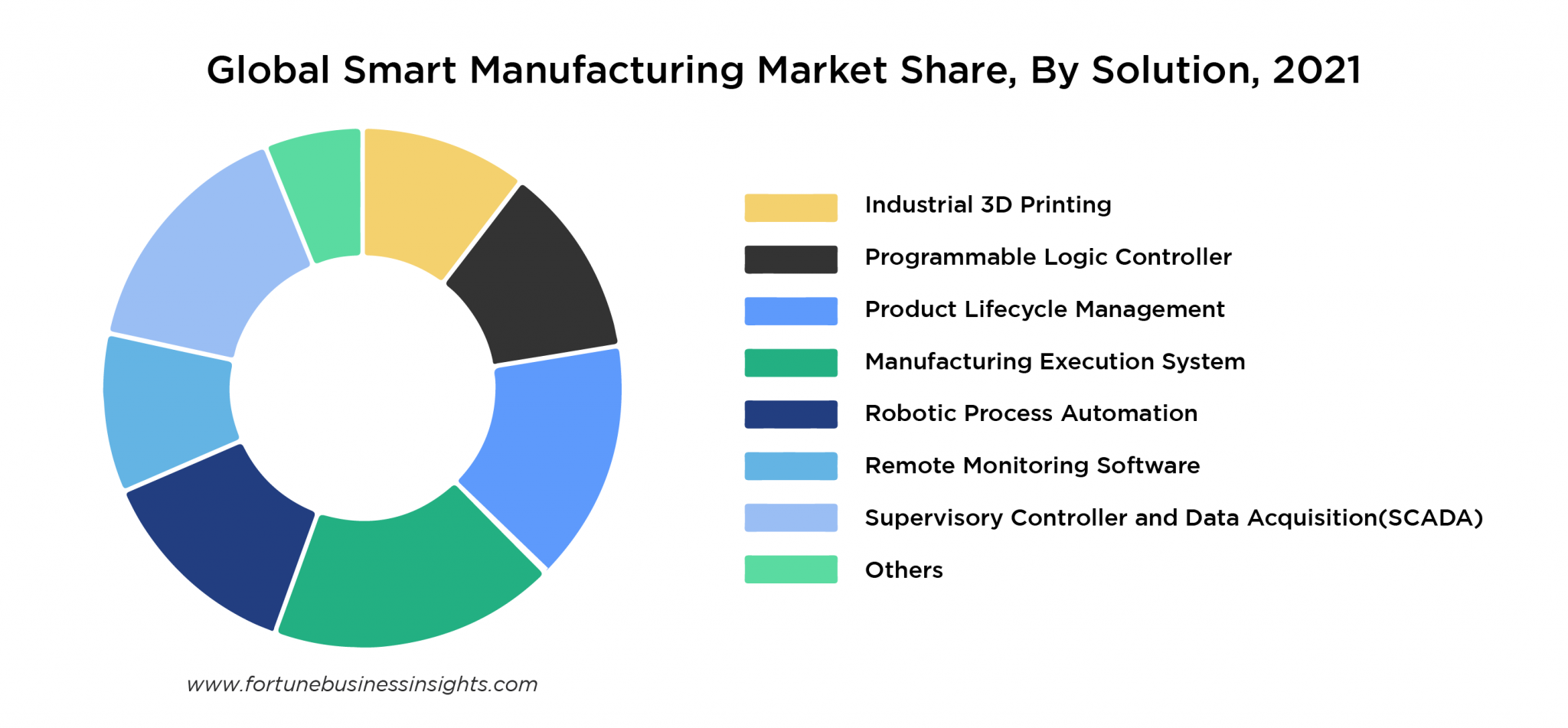
A Guide To Smart Manufacturing
While the benefits and impact of smart manufacturing on overall process visibility, productivity, and cost efficiency are evident, enterprises need to gain a comprehensive understanding of their manufacturing operations, business models, and supply and logistics chains. The findings of these assessments are essential to evaluate whether the establishment of a dynamic production environment such as a smart factory is suitable for them.
- Evaluation of manufacturing operations: Perform a comprehensive review of your operation’s processes and equipment to identify challenges, bottlenecks, opportunities, and limitations. Isolate areas within the operation that are high performing, meeting or exceeding expected KPIs. This will assist you in building a strategic plan to determine the right combination of hardware and ERP.
- Process identification: The processes identified during the previous step will now need to be analyzed on the basis of their performance. Many traditional industrial settings are highly dependent on human resources and are structured to benefit the human personnel and not the productivity of the factory. A deep understanding of these nuances will allow you to formulate strategic plans for the introduction of smart manufacturing technologies to mitigate the challenges that arise from these moving parts.
- Safety parameters: Despite consistent efforts to improve safety practices in factories, accidents and mishaps remain prevalent. It is essential to review safety policies and protocols to determine how smart manufacturing technologies can decrease the likelihood of accidents. It is also useful to look beyond specific safety policies and reports to identify other elements of the operation that impact productivity, safety, cost savings, and uptime.
- Next-gen tools in manufacturing: After deriving insights from the internal review outlined in the steps above, it’s time to look externally to identify tools and equipment that will propel your operation. The key criteria to consider when seeking such tools are scalability, versatility, and flexibility. However, the implementation of such tools into the existing facility should have minimal disturbance due to these factors. Set specific objectives that address fundamental challenges defined in the evaluation phase and ensure solutions allow for integration with other machines and systems.
- Enterprise networks: The culmination of industrial and enterprise networks provides manufacturers with the opportunity to advance business agility and build a unified enterprise-to-plant architecture while increasing visibility, improving troubleshooting, and lowering costs. The architecture of a smart factory involves products and solutions that interact with factory automation systems, enterprise applications, and the wider ecosystem of supplier and partner solutions. Therefore, it is paramount that information technology teams work closely with the operations teams to ensure technical implementations are functional and advantageous to all areas of the enterprise.
- Data security: A smart factory utilizes standard communication protocols to enable machine-to-machine (M2M) communication and life reporting. As a result, secure and reliable communication as well as sophisticated identity and access management of machines and users are essential. As a basic security checklist, networks should include a secure router, firewall, an intrusion prevention system, and wireless IPS. In addition, policy-based access control can be implemented for due diligence.
- Training and integration: Ensure the workforce understands the need for the implementation of smart manufacturing technologies and how their roles will be impacted. Ideally, their responsibilities would pivot to higher-value, more complex tasks. Develop restructuring plans where needed and the training protocols required. Research solution partners to provide guidance and support with communication efforts, integration, and training.
Let’s understand it better with an implementation by Quantiphi for one of the largest food manufacturers in the United States.
Factory Data Migration Leveraging iMDE
One of our customers, an American Fortune 500 branded consumer foods manufacturer, wanted to solve critical issues related to their machine process data accessibility and storage.
The Challenge
The customer faced significant challenges in the utilization of their available machine process data within their existing systems. In particular, insight generation from their cheese-making lines was unstructured, leading to a lack of optimization of their processes. Further, the customer’s storage systems were primarily focused on an on-premises storage strategy and required them to be streamlined with cloud storage options.
In order to address these challenges, Quantiphi leveraged Google’s Intelligent Manufacturing Data Engine.
Google’s Intelligent Manufacturing Data Engine
Google’s Intelligent Manufacturing Data Engine (iMDE) is a contemporary solution that provides a two-pronged approach to smart manufacturing implementation - data analytics and AI-driven operational optimization. Manufacturing analytics and insight generation are facilitated by the iMDE API through Factory Connect, data processing, contextualization, and integration with other Google Cloud Platform services. Relevant use cases like visual inspection, machine-level anomaly detection (identification of red, yellow, and green statuses for equipment based on sensor data and failure metrics), predictive maintenance, root cause identification, and inline quality control are driven by iMDE’s AI-driven operational optimization capabilities. Additionally, iMDE is capable of supporting a variety of data formats from telemetry to images.
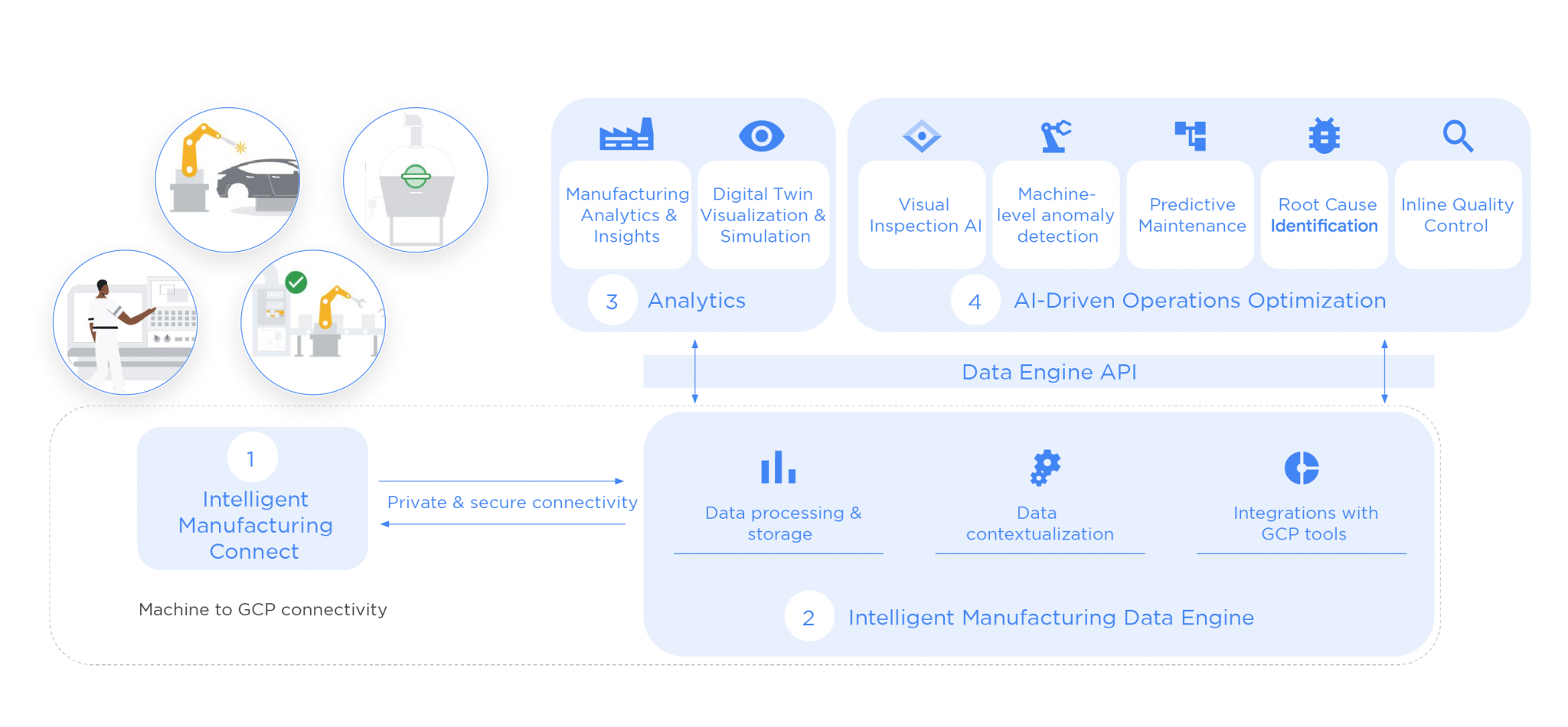
Solution Implementation
Quantiphi’s solution was designed to be capable of connecting multiple production lines across multiple site areas and locations with minimum hassle. Various Intelligent Manufacturing Suite components were installed on the Google Cloud Platform and a pipeline was built to fetch streaming data from the factory connected to BigQuery without changes to the existing system. Quantiphi also implemented Whistle Data Transformation Language to transform JSON input data into data that can be transmitted through Dataflow pipelines. This implementation loads these records to a BigQuery destination to offer insights on data pushed from their manufacturing equipment. Dashboards were built to visualize these insights - Looker for near real-time data analytics of cloud data and Grafana for on-prem data. With future enhancements in mind, Quantiphi also included the Intelligent Manufacturing Suite.
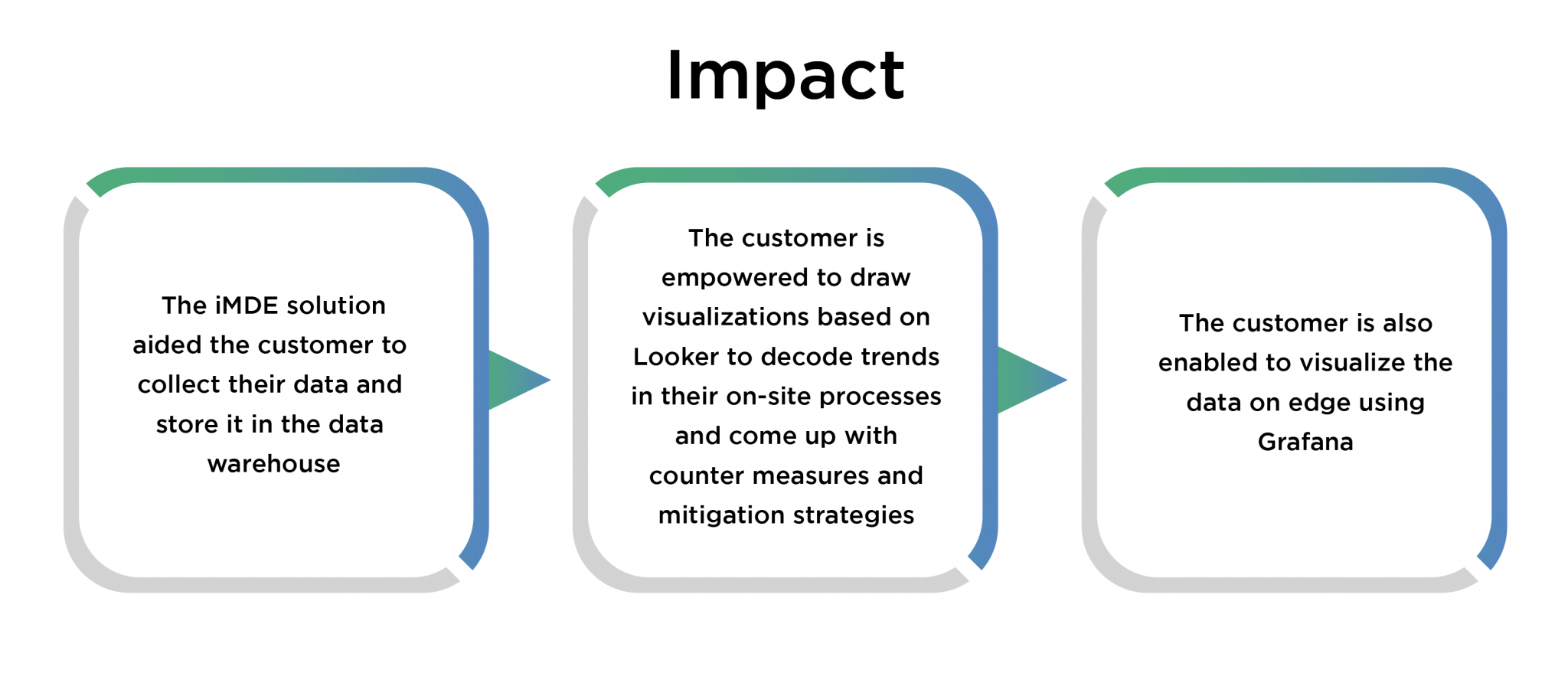
By embracing smart manufacturing technologies, manufacturers can scale new heights in productivity, efficiency, cost savings, and overall facility visibility. Through smart manufacturing, manufacturers can expect higher throughput, dramatically improved uptime, and lower operating costs. In essence, implementing new technologies to improve existing processes will optimize the supply chain. Innovation is risk mitigation to ensure enterprises not only succeed in a competitive and volatile landscape but also grow.
Get in touch with us to transform your operations with smart manufacturing and maximize productivity and cost savings.







